Archivo de noticias y eventos
701 - 750 de un total de 1805
También puede acceder a la lista de noticias publicadas en los medios relacionadas con el Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía - CSIC.
Pages

|
11/05/2015 - 13/05/2015
Workshop estallidos 2015: census and fundamental properties of star-forming galaxies Granada |

|
06/05/2015 - 15:00
Observaciones radiointerferométricas de discos de transición Los discos de transición son discos protoplanetarios con cavidades o huecos en sus zonas internas. Se han sugerido varios mecanismos para explica estas cavidades. El más aceptado y apoyado tanto por simulaciones como por observaciones es el del vaciado de material debido a la interacción gravitatoria del disco con un planeta recién formado. En esta charla explicaré cuáles son los rasgos observacionales característicos de los diferentes... Enrique Macías Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
30/04/2015 - 17:00
Agujeros negros: observando lo invisible Un agujero negro absorbe todo lo que está a su alrededor, incluida la luz, por lo podríamos decir que es un objeto invisible. Sin embargo, sí pueden detectarse sus efectos debido al intenso campo gravitatorio que genera. Antxon Alberdi |

|
30/04/2015 - 14:30
Seven Solutions: industria para las grandes infraestructuras científicas en Granada Seven Solutions es una compañía tecnológica con amplia experiencia diseño de electrónica, software empotrado y mecánica. Colabora con empresas como Indra, Thales, Cibernos, Siemens o National Instruments. Seven Solutions cuenta con una dilatada experiencia en el campo de la industria de la ciencia, participando activamente en iniciativas open hardware como el OHWR.org.... Javier Díaz Alonso |

|
16/04/2015 - 14:30
The San Pedro Mártir observatory and its UBVRI photometric survey of Galactic clusters A short presentation of the San Pedro Martir Observatory will be given including its astroclimatic characteristics and its projects for the near future. I will then present the current status of our ongoing survey aimed at generating a homogeneous catalogue of physical parameters of stellar clusters in our Galaxy. It is expected that this data will allow the study of the properties of the galactic disk more accurately and reliability, helping... Raul Michel Murillo |

|
09/04/2015 - 14:30
Ionized gas in the CALIFA galaxies We present here the most recent results we have obtained in our exploration of the gas abundances using the IFU data from the CALIFA survey. Using our own developed tools we have extracted the ionized gas properties of ~10.000 HII regions, in order to explore: (i) the relation between these properties and those of the host galaxies and the underlying stellar population; (ii) the local relation between the gas... Sebastian Sanchez |

|
26/03/2015 - 18:00
Astronomía y literatura ¿Tiene sentido esta mezcla? A tenor de las páginas que ya existen en la red, incluso parece que la idea está muy extendida. ¿Qué hace la Astronomía y qué hace la Literatura? En ambos casos, el científico y el escritor tratan de darnos su visión del mundo, son aproximaciones humanas a un entorno desconocido y a veces desconcertante. El primero trata de explicar, el segundo de conmover, pero ambos conmueven y explican. Emilio J. Alfaro y Susana Escudero |

|
26/03/2015 - 13:30
FROM ALHAMBRA TO JAVALAMBRE. A SCIENTIFIC PROJECT The Observatorio Astrofísico de Javalambre, with its 2 very wide field telescopes has been purposely built to conduct large scale surveys. The use of medium-narrow band filters, pioneered by the ALHAMBRA project, will produce a low resolution spectrum of every pixel in the sky. The first defined projects, J-PLUS@T80 and J-PAS@T250 are driven by the study of the nearby Universe and the study of dark energy... Prof. Mariano Moles Villamate |

|
25/03/2015 - 17:00
Charla especial en recuerdo a Manuel Félix. El fotón viajero: un paseo por los planetas. Manuel Félix Herrera Gómez hizo el Trabajo Fin de Máster (TFM) con el grupo de José Luis Ortiz y empezó su tesis en el grupo de Manuel Lopez Puertas. Con motivo de recordar su memoria los estudiantes de doctorado del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía hemos querido que las charlas realizadas por nosotros lleven su nombre. Además, en 2003 tuvo lugar el descubrimiento del asteroide 2003 ES desde el Observatorio de Sierra Nevada,... Francisco José Pozuelos Romero, Estela del Mar Fernández Valenzuela y Zaira Modroño Berdiñas Salón de Actos del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
12/03/2015 - 13:30
AirPlay Service The Computer Center has launched a new service called AirPlay with aim of provide the users the projection of multimedia contents via wireless (WiFi). This will allow to make presentations from laptops or mobile devices without the need of any wiring connection, contributing greater ease and mobility to the speaker. In this seminar will explain the configuration and use procedures of the AirPlay service for devices with Android, iOS, OS X,... Francisco Manuel Bayo Muñoz |

|
05/03/2015 - 13:30
Understanding the obscuring torus and the nuclear star formation of AGN using GTC/CanariCam observations The fueling of black holes occurring in active galactic nuclei (AGN) is fundamental to the evolution of galaxies. AGN themselves are largely explained in the context of a unified theory, by which a geometrically and optically thick torus of gas and dust obscures the AGN central engine. The torus intercepts a substantial amount of flux from the central engine and and reradiates it in the infrared. There are still many... Almudena Alonso-Herrero |

|
26/02/2015 - 18:00
¿Por qué nos importan las formas de las galaxias? Las galaxias aparecen en el universo con formas distintas (unas son más esféricas, otras elípticas, espirales, o totalmente irregulares), y con una gran diversidad de estructuras (bulbos, discos, barras nucleares, brazos espirales, anillos, colas, etc). Estudiar estas propiedades morfológicas de las galaxias es justamente uno de los parámetros clave para entender cómo se forman y evolucionan. Mirjana Povic |

|
19/02/2015 - 13:30
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COSMIC DUST: THE NANOCOSMOS PROJECT Evolved stars are the factories of cosmic dust. This dust is made of tiny grains that are injected into the interstellar medium and plays a key role in the evolution of astronomical objects from galaxies to the embryos of planets. However, the fundamental processes involved in dust formation and evolution are still a mystery. The aim of the NANOCOSMOS project is to take advantage of the new ... J. Cernicharo, C. Joblin & J.A. Gago |

|
16/02/2015 - 13:30
Activity and Evolution of Oort Cloud Comets Comets formed early in the evolution of the solar system while material was accreting to form planets. When proto-planets became large enough, a population of comets was dynamically ejected into the Oort cloud. Comets entering the inner solar system for the first time are called dynamically new comets. These objects have not been heated by the Sun and retain some of the most primordial material available for observation in the solar system... Dr. Dennis Bodewits |

|
29/01/2015 - 18:00
Historia de un planeta canijo (o elogio de la soberbia)” La misión Solar Orbiter ocupa el lugar M1 del programa Cosmic Vision de la ESA. Se trata de una nave que orbitará el Sol con órbitas muy elípticas cuya mínima distancia al Sol será tan pequeña como la del radio medio de la órbita de Mercurio: tan solo un 30 % de la distancia entre la Tierra y el Sol. Dichas órbitas, además, se elevarán del plano de la eclíptica hasta 35º con lo que ofrecerán una visión inédita de los polos del Sol. Jose Carlos del Toro Iniesta |

|
18/12/2014 - 18:00
Visitamos un cometa. El éxito de la misión Rosetta Tras recorrer casi seis mil cuatrocientos millones de kilómetros a través del Sistema Solar, la sonda Rosetta (ESA) ha completado varios hitos en la exploración espacial: despertó con éxito tras meses en hibernación, se colocó en órbita en torno al cometa 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko y liberó un módulo robótico, Philae, que se posó sobre el núcleo del cometa... Pedro J. Gutiérrez y José Juan López Moreno |

|
11/12/2014 - 13:30
Structural properties of isolated galaxies Distinct components of galaxies are products of internal and environmental processes throughout their lifetimes. Disentangling these processes is an important issue for understanding how galaxies form and evolve. In this context isolated galaxies represent a fruitful population to explore as they should be mainly affected by internal processes (minimal merger/accretion/tidal effects). I will present the structural analysis of a representative... Mirian Fernández Lorenzo |

|
04/12/2014 - 13:30
GLORIA: Global Robotic Intelligent Array for e-science Dr. Alberto J. Castro-Tirado |

|
04/12/2014 - 13:30
GLORIA: Global Robotic Intelligent Array for e-science GLORIA is an FP7 project (UE-funded in 2011-14) hosted by 14 institutions (including several Spanish OPIs and Universities) based on a collaborative web 2.0 which allows to access 14 robotic telescopes worldwide with a diameter in the range 0.25-0.60 m. The goal is to grant the GLORIA users community (from citizens to amateur astronomers) participation in Citizen Science activities. To achieve this, experiments have... Prof. Dr. Alberto J. Castro-Tirado |

|
28/11/2014 - 17:00
75 aniversario CSIC. Sesión con cinco investigadores Para conocer mejor al principal organismo público de investigación en España, hablarán sus protagonistas, algunos de los científicos y científicas que en el hacen investigación. CSIC |

|
27/11/2014 - 13:30
Energetic transients as a part of time domain astronomy in TMT era Study of energetic cosmic explosions as a part of time domain astronomyis one of the key areas that could be pursued with upcoming Giant segmented optical-IR telescopes with a very large photon collecting area applying cutting edge technology. Existing 8-10m class telescopes have been helpful to improve our knowledge about Core-Collapse Supernovae, Gamma-ray Bursts and nature of their progenitors and explosion... S. B. Pandey |

|
24/11/2014 - 13:30
First results from SDSS IV - MaNGA Large spectroscopic surveys of nearby galaxies (like the Sloan Digital Sky Survey) have shaped our understanding of galaxy evolution. However, to gain insight into the processes shaping the various galactic sub-components, a three-dimensional view (giving access to both spatial and spectral information) is necessary. In recent years, integral field spectroscopy (IFS) surveys of the nearby Universe (Sauron, CALIFA, Sami) are filling in this... Francesco Belfiore |

|
20/11/2014 - 13:00
An ALMA view on the compact obscured nuclei of luminous IR galaxies Until recently, the study of the molecular interstellar medium of galaxies has been mostly focused on a few, relatively abundant, molecular species. Recent attempts at modeling the molecular emission of active galaxies have shown that standard high-density tracers do not provide univocal results and are not able to discriminate between different relevant environments (e.g., star-formation vs AGN). Spectral lines surveys allow us to explore... Francesco Costagliola |

|
13/11/2014 - 13:30
Unveiling the Massive Stars in the Galactic Centre Because of the proximity, the Galactic Centre is an unique lab for studies of the interplay between stars, ISM and super massive black holes in galactic nuclei. The central 200 pc of the Galactic Centre includes 4x10^7 molecular clouds and has a star formation rate of ~0.03 M/yr. Three young, massive and compact star clusters were found and includes around 100 massive stars, which shape the nearby ISM. However, the... Dr. Hui Dong |

|
30/10/2014 - 18:00
La cuna de la vida: cómo se forman las estrellas y los planetas Hace casi veinte años que se descubrió el primer exoplaneta, pero desde mucho antes los astrónomos que estudiamos cómo se forman la estrellas ya teníamos evidencias de que otras estrellas como el Sol podían estar rodeadas de sistemas planetarios. Las estrellas se forman a partir del colapso de nubes enormes de gas y polvo. En este proceso, la estrella acaba rodeada de un disco en rotación a su alrededor. Mayra Osorio |

|
30/10/2014 - 13:30
The non-thermal universe at the highest energies: TeV gamma-ray astronomy with the MAGIC telescope Some os the most violent processed in the universe present a non-thermal spectrum reaching energies of several tens of TeV. Due to the low fluxes at these energies, we need a technique capable to achieve collection areas of the order of the km^2. This can be reached by the Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov technique and MAGIC is one of the main detectors for performing ground-based observations using this technique. It consists of two 17m... Rubén López-Coto |

|
23/10/2014 - 23/10/2014
Spanish SKA Day Granada |

|
22/10/2014 - 14:30
High Frequency Astrometry and Pulsar Studies with the Korean VLBI Network Maria Rioja will report on the Korean VLBI Network (KVN), the first dedicated mm-VLBI array. The 3 telescopes have an innovative multifrequency receiver that allows for simultaneous observations at 22, 43, 86 &129GHz. With care these can be phase referenced to allow astrometry at these frequencies. I will show our first results of phase referencing at 132GHz and the path to compatible global VLBI. Richard Dodson will discuss a... María Rioja and Richard Dodson |

|
17/10/2014 - 09:30
Monte Carlo models of the dust environment of a sample of comets from the Oort Cloud to the outer main asteroid belt En esta tesis presentamos nuestros estudios realizados sobre diferentes familias cometarias. Veremos resultados sobre la Familia de Júpiter, población a la que pertenece el objetivo de la actual misión Rosetta, el 67P/C-G. Estudios llevados a cabo para poder determinar el mecanismo de activación de los misteriosos cometas del Cinturón Principal, los cuales podrían encerrar las claves para entender... Francisco Pozuelos Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
16/10/2014 - 14:30
The Fingerprint of a Galactic Nucleus: A Multi-Wavelength, High-Angular Resolution, Near Infrared Study of the Centre of the Milky Way The centre of the Milky Way is the only galactic nucleus and the most extreme astrophysical environment that we can examine on scales of milli-parsecs. It is therefore a crucial laboratory for studying galactic nuclei and their role in the context of galaxy evolution. Yet, suitable data that would allow us to examine the stellar component of the Galactic Centre exist for less than 1% of its projected area. This ERC-funded research programme... Dr. Rainer Schödel |

|
15/10/2014 - 15:00
X-ray emission from hot bubbles in Nebulae around Evolved Stars I present the observational and numerical results of my phd thesis developed in the past three years. These results account for high-quality X-ray observations of diffuse X-ray emission in Wolf-Rayet nebulae and planetary nebulae (PNe) in comparison with optical and infrared observations. Our numerical simulations were tailored to study the formation, evolution, and X-ray emission from PNe. These results help us study the role of instabilities... Jesús A. Toalá Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
15/10/2014 - 14:30
OCTOCAM: Proposal for a multichannel imager and spectrograph with high-time-resolution capabilities for the 8.1m Gemini telescopes OCTOCAM is a multichannel imager and spectrograph that we will be proposing in the months to come for the 8.1m Gemini telescopes, in response to a call for feasibility studies of new instruments that has been recently opened. It will use dichroics to split the incoming light to obtain simultaneous observations in 8 different bands, from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. In its imaging mode, it will have a field of view of around 3'x3... Dr. Antonio de Ugarte Postigo |
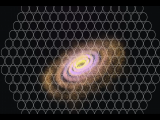
|
30/09/2014
Una visión sin precedentes de doscientas galaxias del universo local Hoy tendrá lugar la segunda emisión pública de datos del proyecto CALIFA, un muestreo de galaxias desarrollado en el Observatorio de Calar Alto |

|
24/09/2014 - 14:30
Metamateriales Quirales, el Plan B para la Refracción Negativa Metamateriales, más allá de los materiales, con este término se engloba una amplia variedad de materiales artificiales cuyas propiedades van más allá de las que nos proporciona la naturaleza. Mayor resistencia, extremada ligereza, propiedades exóticas o comportamientos anómalos ante la radiación son algunas de las características que estamos buscando. En esta charla... Dr. Gregorio José Molina Cuberos |

|
03/07/2014 - 14:30
'What is the progenitor system of the nearby Type Ia SN 2014J?' Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) are the thermonuclear explosive end-products of white dwarfs. SNe Ia are primary cosmological distance indicators and a major contributor to the chemical evolution of galaxies, yet we do not know what makes a SN Ia. There are two basic families of models leading to a SN Ia, the single- degenerate model (SD) and the double-degenerate model (DD). In the SD scenario, a WD... Dr. Miguel Ängel Pérez Torres |

|
30/06/2014 - 01/07/2014
Workshop for the WSO Working Group and Spanish UV Astronomy Granada |

|
26/06/2014 - 17:00
La muerte de las estrellas La charla comenzará describiendo qué es una estrella, cómo se forma y evoluciona y, dependiendo de sus características, cuál será su final. Nos detendremos en la fase de nebulosa planetaria y trataremos el enriquecimiento químico del medio interestelar. Alejandro Márquez Lugo |

|
26/06/2014 - 14:30
The brief lives of massive stars as witnessed by interferometry Massive stars present the newest and perhaps most challenging opportunity for long baseline interferometry to excel. Large distances require high angular resolution both to study the means of accreting enough mass in a short time and to split new-born multiples into their components for the determination of their fundamental parameters. Dust obscuration of young stellar objects require interferometry in the infrared, while post-... Dr. Christian Hummel |

|
24/06/2014 - 14:30
Remote sensing: survival strategies in the jungle of averaging kernels and covariance matrices Outer space, stars, exoplanets, planets in the solar system, and even the Earth's middle and upper atmosphere have in common that it is inconvenient, expensive, and often technically unfeasible to make in situ measurements there. Remote sensing, e.g., by means of radiance measurements, is a relatively cheap and convenient alternative. The conversion of the measured radiances to the quantities of interest, e.g., temperature and composition... Dr. Thomas von Clarmann |

|
11/06/2014 - 10:00
La evolución temporal de la convección en la penumbra de las manchas solares El Sol presenta varias incógnitas todavía sin resolver. Una de ellas es la conocida como el calentamiento penumbral. La penumbra es una región brillante cuya intensidad llega a ser aproximadamente del 75% de la del Sol en calma, incluso teniendo un campo magnético fuerte. A pesar de los esfuerzos realizados por numerosos autores aún no se conoce cómo se transporta la energía en la... Sara Esteban Pozuelo Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
05/06/2014 - 14:30
Status of Astronomy in East Africa Activities of astronomy in East Africa are driven the East African Astronomical Society (EAAS) supported mainly by the IAU/OAD. A positive trend in the development of astronomy activities in the region is characterised by the inclusion of astronomy into the curriculum at all levels, construction of astronomy observatories and research centres (e.g. Entoto Observatory -first light last week), opening new MSc... Dr. Pheneas Nkundabakura |

|
29/05/2014 - 17:00
Enigma. La máquina de los secretos La máquina Enigma, utilizada en la II Guerra Mundial por el ejército alemán para el cifrado de todas sus comunicaciones, se ha convertido en un icono de la ingeniería de todos los tiempos. Álvaro Martínez Sevilla |

|
29/05/2014 - 14:30
IAA Computing Service A cluster is defined as a collection of interconnected stand-alone workstations or PCs cooperatively working together as a single, integrated computing resource. Cluster Computing has become the paradigm of choice for executing large-scale science, engineering, and commercial applications. This is due to their low cost, high performance, availability of off-the-shelf hardware components and freely accessible software tools that that can be... Rafael Parra |

|
15/05/2014 - 14:30
Deep spectroscopy of planetary nebulae In nebulae astrophysics, there are two long-standing discrepancies: 1) the ionic and elemental abundances of C, N, O, and Ne derived from optical recombination lines (ORLs) are systematically higher than those derived from collisionally excited lines (CELs); 2) the electron temperature derived from H I recombination continuum (e.g., Balmer jump at 3646 A) is always lower than that derived from CELs. These two... Dr. Xuan Fang |

|
14/05/2014 - 08:00
Qué es una partícula II: Hawking versus Unruh Esta charla pretende ser una introducción divulgativa a algunos de los fenómenos de la denominada Teoría Cuántica de Campos en espacios curvos. Las dos teorías físicas que, a fecha de hoy, describen las leyes de la naturaleza a un nivel más fundamental son la Relatividad General para el campo gravitatorio, y la Teoría Cuántica de Campos para el resto de campos físicos,... Luis Cortés Barbado Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
24/04/2014 - 17:00
Inflación cósmica y modos B. Los instantes posteriores al Big Bang Hace unas semanas se hacía pública la detección de polarización de tipo magnética en la radiación cósmica de microondas. Esta observación proporciona fuertes indicios de la presencia de ondas gravitacionales en tiempos remotos y podría confirmar la teoría inflacionaria del origen del universo. En esta charla se explicará qué es lo que se ha visto y sus posibles implicaciones. Carlos Barceló y Eduardo Battaner |

|
24/04/2014 - 14:30
Inconsistences in the harmonic analysis of time series The power of asteroseismology relies on the ability to infer the stellar structure from the unambiguous frequency identification of the correspoinding pulsation mode. Hence, the use of a Fourier transform is in the basis of asteroseismic studies. Nevertheless, the difficulties with the interpretation of the frequencies found in many stars lead us to reconsider Fourier analysis and the classical methods used to process time series... Javier Pascual Granado |

|
23/04/2014 - 10:00
About Mars, its atmosphere and the dust El planeta Marte, con su color rojizo, siempre ha despertado la imaginación de la mente humana en diferentes culturas. Ha sido asociado al dios de la guerra, la destrucción y el inframundo. Ya no tenemos miedo a Marte ni a los marcianos como se tenía antaño, nuestra preocupación ahora es si nuestras naves llegarán al planeta rojo. Este fantástico planeta, el cual estamos descubriendo, tiene la... Dominika Dabrowska Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
10/04/2014 - 14:30
Sculpting the Galactic Centre: Astrophysics and fundamental physics with photons and gravitational waves Since 1993 we have known that the Galactic Center (GC) displays a core-like distribution of red giant branch (RGB) stars starting at ~ 1'', which poses a theoretical problem, because the GC should have formed a segregated cusp of old stars. I postulate that the reason for the missing stars in the RGB is closely intertwined with the formation of a formerly existing dense gas disk, an episode that removed the... Dr. Pau Amaro-Seoane |

|
09/04/2014 - 09:30
'El hombre en la Luna: ¿una gran producción de NASA o de Hollywood? Resumen: Aprendemos en el colegio que el momento culminante del siglo XX fue la llegada del hombre a la Luna. Sin embargo, las limitaciones técnicas de la época, junto con la necesidad urgente que tenían los Estados Unidos de no dejarse vencer por Rusia en la carrera espacial podrían haber justificado lo que muchos afirman que es el mayor fraude de la historia de la Humanidad. En esta charla mostrar... Javier Peralta Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |