Headlines and events archive
Displaying 901 - 950 of 1931
You may also find an archive of news published in the media which are related with the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía - CSIC.
Pages

|
24/02/2015
The huge “Y” in the atmosphere of Venus due to a wave distorted by the wind When observed in the ultraviolet range, Venus’ atmosphere reveals to be covered by a dark Y-shaped cloud whose origin and evolution have remained unexplained up to date |

|
19/02/2015 - 13:30
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COSMIC DUST: THE NANOCOSMOS PROJECT Evolved stars are the factories of cosmic dust. This dust is made of tiny grains that are injected into the interstellar medium and plays a key role in the evolution of astronomical objects from galaxies to the embryos of planets. However, the fundamental processes involved in dust formation and evolution are still a mystery. The aim of the NANOCOSMOS project is to take advantage of the new ... J. Cernicharo, C. Joblin & J.A. Gago |
|
19/02/2015
The origin of the magnetic field covering the Sun has been discovered High resolution observations using the HINODE satellite reveal the existence of small magnetic elements inside solar supergranules |

|
18/02/2015
JUPITER, a laboratory for studying exoplanets Its atmosphere has been analized during an eclipse of Ganymede, the third satellite of the gas giant |

|
16/02/2015 - 13:30
Activity and Evolution of Oort Cloud Comets Comets formed early in the evolution of the solar system while material was accreting to form planets. When proto-planets became large enough, a population of comets was dynamically ejected into the Oort cloud. Comets entering the inner solar system for the first time are called dynamically new comets. These objects have not been heated by the Sun and retain some of the most primordial material available for observation in the solar system... Dr. Dennis Bodewits |

|
16/02/2015
The highest plume ever observed on Mars Researchers are studying images of a mysterious bulge that rose up more than 200 km from the surface |

|
16/02/2015
Stars akin to the sun also explode when they die IRAS 15103-5754, a star observed as it was turning into a planetary nebula, yields new clues as to the death of stars akin to the sun |

|
27/01/2015
The characteristics of the multiple star "sigma Orionis" are determined A detailed study on the multiple star system led by Spanish astrophysicists has identified the period, mass and emission of high energy photons of the main stars of the system |

|
22/01/2015
Rosetta mission yields most accurate and integral picture of a comet ever Science magazine publishes special edition on findings of Rosetta, on orbit around comet 67P Churyumov-Gerasimenko since August 2014 |

|
11/12/2014 - 13:30
Structural properties of isolated galaxies Distinct components of galaxies are products of internal and environmental processes throughout their lifetimes. Disentangling these processes is an important issue for understanding how galaxies form and evolve. In this context isolated galaxies represent a fruitful population to explore as they should be mainly affected by internal processes (minimal merger/accretion/tidal effects). I will present the structural analysis of a representative... Mirian Fernández Lorenzo |
|
10/12/2014
A universal comb Optical frequency comb allows more accurate astronomical observations |

|
04/12/2014 - 13:30
GLORIA: Global Robotic Intelligent Array for e-science Dr. Alberto J. Castro-Tirado |

|
04/12/2014 - 13:30
GLORIA: Global Robotic Intelligent Array for e-science GLORIA is an FP7 project (UE-funded in 2011-14) hosted by 14 institutions (including several Spanish OPIs and Universities) based on a collaborative web 2.0 which allows to access 14 robotic telescopes worldwide with a diameter in the range 0.25-0.60 m. The goal is to grant the GLORIA users community (from citizens to amateur astronomers) participation in Citizen Science activities. To achieve this, experiments have... Prof. Dr. Alberto J. Castro-Tirado |

|
27/11/2014 - 13:30
Energetic transients as a part of time domain astronomy in TMT era Study of energetic cosmic explosions as a part of time domain astronomyis one of the key areas that could be pursued with upcoming Giant segmented optical-IR telescopes with a very large photon collecting area applying cutting edge technology. Existing 8-10m class telescopes have been helpful to improve our knowledge about Core-Collapse Supernovae, Gamma-ray Bursts and nature of their progenitors and explosion... S. B. Pandey |

|
24/11/2014 - 13:30
First results from SDSS IV - MaNGA Large spectroscopic surveys of nearby galaxies (like the Sloan Digital Sky Survey) have shaped our understanding of galaxy evolution. However, to gain insight into the processes shaping the various galactic sub-components, a three-dimensional view (giving access to both spatial and spectral information) is necessary. In recent years, integral field spectroscopy (IFS) surveys of the nearby Universe (Sauron, CALIFA, Sami) are filling in this... Francesco Belfiore |

|
20/11/2014 - 13:00
An ALMA view on the compact obscured nuclei of luminous IR galaxies Until recently, the study of the molecular interstellar medium of galaxies has been mostly focused on a few, relatively abundant, molecular species. Recent attempts at modeling the molecular emission of active galaxies have shown that standard high-density tracers do not provide univocal results and are not able to discriminate between different relevant environments (e.g., star-formation vs AGN). Spectral lines surveys allow us to explore... Francesco Costagliola |

|
13/11/2014 - 13:30
Unveiling the Massive Stars in the Galactic Centre Because of the proximity, the Galactic Centre is an unique lab for studies of the interplay between stars, ISM and super massive black holes in galactic nuclei. The central 200 pc of the Galactic Centre includes 4x10^7 molecular clouds and has a star formation rate of ~0.03 M/yr. Three young, massive and compact star clusters were found and includes around 100 massive stars, which shape the nearby ISM. However, the... Dr. Hui Dong |

|
11/11/2014
IAA-CSIC is co-managing an instrument that will orbit around the Sun on board the Solar Orbiter mission (ESA) Solar Orbiter (ESA) will travel around the Sun to study both solar physics and the Sun’s influence on the interplanetary medium, using instruments of local measurement as well as remote surveyal |

|
10/11/2014
The GLORIA Project makes available to internet users 13 robotic telescopes in three continents GLORIA, which uses copyleft licenses for the free distribution of its contents and materials, is supported by the Ciziten Science program of the European Union |

|
30/10/2014 - 13:30
The non-thermal universe at the highest energies: TeV gamma-ray astronomy with the MAGIC telescope Some os the most violent processed in the universe present a non-thermal spectrum reaching energies of several tens of TeV. Due to the low fluxes at these energies, we need a technique capable to achieve collection areas of the order of the km^2. This can be reached by the Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov technique and MAGIC is one of the main detectors for performing ground-based observations using this technique. It consists of two 17m... Rubén López-Coto |

|
29/10/2014
Existence of a group of “quiet” quasars confirmed Apart from very distant, ultraluminous quasars -evolving rapidly and associated with galaxy mergers - there is likely another population of quasars that evolves slowly |

|
23/10/2014 - 23/10/2014
Spanish SKA Day Granada |

|
22/10/2014 - 14:30
High Frequency Astrometry and Pulsar Studies with the Korean VLBI Network Maria Rioja will report on the Korean VLBI Network (KVN), the first dedicated mm-VLBI array. The 3 telescopes have an innovative multifrequency receiver that allows for simultaneous observations at 22, 43, 86 &129GHz. With care these can be phase referenced to allow astrometry at these frequencies. I will show our first results of phase referencing at 132GHz and the path to compatible global VLBI. Richard Dodson will discuss a... María Rioja and Richard Dodson |

|
17/10/2014 - 09:30
Monte Carlo models of the dust environment of a sample of comets from the Oort Cloud to the outer main asteroid belt En esta tesis presentamos nuestros estudios realizados sobre diferentes familias cometarias. Veremos resultados sobre la Familia de Júpiter, población a la que pertenece el objetivo de la actual misión Rosetta, el 67P/C-G. Estudios llevados a cabo para poder determinar el mecanismo de activación de los misteriosos cometas del Cinturón Principal, los cuales podrían encerrar las claves para entender... Francisco Pozuelos Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
16/10/2014 - 14:30
The Fingerprint of a Galactic Nucleus: A Multi-Wavelength, High-Angular Resolution, Near Infrared Study of the Centre of the Milky Way The centre of the Milky Way is the only galactic nucleus and the most extreme astrophysical environment that we can examine on scales of milli-parsecs. It is therefore a crucial laboratory for studying galactic nuclei and their role in the context of galaxy evolution. Yet, suitable data that would allow us to examine the stellar component of the Galactic Centre exist for less than 1% of its projected area. This ERC-funded research programme... Dr. Rainer Schödel |

|
15/10/2014 - 15:00
X-ray emission from hot bubbles in Nebulae around Evolved Stars I present the observational and numerical results of my phd thesis developed in the past three years. These results account for high-quality X-ray observations of diffuse X-ray emission in Wolf-Rayet nebulae and planetary nebulae (PNe) in comparison with optical and infrared observations. Our numerical simulations were tailored to study the formation, evolution, and X-ray emission from PNe. These results help us study the role of instabilities... Jesús A. Toalá Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
15/10/2014 - 14:30
OCTOCAM: Proposal for a multichannel imager and spectrograph with high-time-resolution capabilities for the 8.1m Gemini telescopes OCTOCAM is a multichannel imager and spectrograph that we will be proposing in the months to come for the 8.1m Gemini telescopes, in response to a call for feasibility studies of new instruments that has been recently opened. It will use dichroics to split the incoming light to obtain simultaneous observations in 8 different bands, from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. In its imaging mode, it will have a field of view of around 3'x3... Dr. Antonio de Ugarte Postigo |
|
30/09/2014
An unprecedented view of two hundred galaxies of the local Universe The second data release of the international project CALIFA - a survey of galaxies carried out at Calar Alto observatory – will take place today |

|
24/09/2014 - 14:30
Metamateriales Quirales, el Plan B para la Refracción Negativa Metamateriales, más allá de los materiales, con este término se engloba una amplia variedad de materiales artificiales cuyas propiedades van más allá de las que nos proporciona la naturaleza. Mayor resistencia, extremada ligereza, propiedades exóticas o comportamientos anómalos ante la radiación son algunas de las características que estamos buscando. En esta charla... Dr. Gregorio José Molina Cuberos |

|
23/09/2014
Signs of the formation of a planetary system around the star HD169142 Young star HD169142 displays a disk of gas and dust with two annular gaps possibly due to the formation of planets |

|
20/08/2014
Type Ia supernovae stem from the explosion of white dwarfs coupled with twin stars Study discards possibility that type Ia supernovae might stem from explosions of white dwarfs nourished by normal stars. Were these conclusions to become generalized, type Ia supernovae might no longer serve as “standard candles” to measure astronomical distances |
|
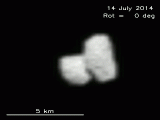
17/07/2014
The unexpected shape of the nucleus of the comet 67P Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, destination of ESA’s Rosetta mission, seems to consist of two parts |

|
09/07/2014
The atmospheric waves of Venus, key to understanding the superrotation of its atmosphere, have been deciphered Venus’ atmosphere rotates up to sixty times faster than its surface, a phenomenon known as superrotation whose origin hast yet to be satisfactorily explained |

|
03/07/2014 - 14:30
'What is the progenitor system of the nearby Type Ia SN 2014J?' Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) are the thermonuclear explosive end-products of white dwarfs. SNe Ia are primary cosmological distance indicators and a major contributor to the chemical evolution of galaxies, yet we do not know what makes a SN Ia. There are two basic families of models leading to a SN Ia, the single- degenerate model (SD) and the double-degenerate model (DD). In the SD scenario, a WD... Dr. Miguel Ängel Pérez Torres |
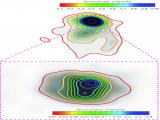
|
03/07/2014
Researchers from the IAA win the "Beauty Contest", an international competition to obtain optical/infrarred interferometric images Imaging at optical/infrared wavelengths is a novel technique that has been developed during the last ten years |

|
03/07/2014
Rosetta’s comet takes shape In current images obtained by OSIRIS, Rosetta’s scientific imaging system, the nucleus of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko covers good four pixels |

|
02/07/2014
IMaX, a Spanish instrument, reveals how magnetic structures in the Sun are born and evolve IMaX, aboard the SUNRISE mission –a telescope that observed the sun from a stratospheric balloon over the Arctic- has observed the formation and evolution of a magnetic flux tube on the solar surface |

|
30/06/2014 - 01/07/2014
Workshop for the WSO Working Group and Spanish UV Astronomy Granada |

|
26/06/2014 - 14:30
The brief lives of massive stars as witnessed by interferometry Massive stars present the newest and perhaps most challenging opportunity for long baseline interferometry to excel. Large distances require high angular resolution both to study the means of accreting enough mass in a short time and to split new-born multiples into their components for the determination of their fundamental parameters. Dust obscuration of young stellar objects require interferometry in the infrared, while post-... Dr. Christian Hummel |

|
24/06/2014 - 14:30
Remote sensing: survival strategies in the jungle of averaging kernels and covariance matrices Outer space, stars, exoplanets, planets in the solar system, and even the Earth's middle and upper atmosphere have in common that it is inconvenient, expensive, and often technically unfeasible to make in situ measurements there. Remote sensing, e.g., by means of radiance measurements, is a relatively cheap and convenient alternative. The conversion of the measured radiances to the quantities of interest, e.g., temperature and composition... Dr. Thomas von Clarmann |

|
11/06/2014 - 10:00
La evolución temporal de la convección en la penumbra de las manchas solares El Sol presenta varias incógnitas todavía sin resolver. Una de ellas es la conocida como el calentamiento penumbral. La penumbra es una región brillante cuya intensidad llega a ser aproximadamente del 75% de la del Sol en calma, incluso teniendo un campo magnético fuerte. A pesar de los esfuerzos realizados por numerosos autores aún no se conoce cómo se transporta la energía en la... Sara Esteban Pozuelo Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
05/06/2014 - 14:30
Status of Astronomy in East Africa Activities of astronomy in East Africa are driven the East African Astronomical Society (EAAS) supported mainly by the IAU/OAD. A positive trend in the development of astronomy activities in the region is characterised by the inclusion of astronomy into the curriculum at all levels, construction of astronomy observatories and research centres (e.g. Entoto Observatory -first light last week), opening new MSc... Dr. Pheneas Nkundabakura |

|
04/06/2014
Ancient worlds around a "foreign" star Two planets have been discovered around Kapteyn´s, a star that was possibly part of a satellite galaxy absorbed by the Milky Way |

|
29/05/2014 - 14:30
IAA Computing Service A cluster is defined as a collection of interconnected stand-alone workstations or PCs cooperatively working together as a single, integrated computing resource. Cluster Computing has become the paradigm of choice for executing large-scale science, engineering, and commercial applications. This is due to their low cost, high performance, availability of off-the-shelf hardware components and freely accessible software tools that that can be... Rafael Parra |
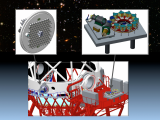
|
21/05/2014
The contract for the construction of MEGARA, the next optical instrument for the Gran Telescopio Canarias, is signed MEGARA is the first spectrograph capable of observing the emission of the gas located in between distant galaxies |

|
15/05/2014 - 14:30
Deep spectroscopy of planetary nebulae In nebulae astrophysics, there are two long-standing discrepancies: 1) the ionic and elemental abundances of C, N, O, and Ne derived from optical recombination lines (ORLs) are systematically higher than those derived from collisionally excited lines (CELs); 2) the electron temperature derived from H I recombination continuum (e.g., Balmer jump at 3646 A) is always lower than that derived from CELs. These two... Dr. Xuan Fang |

|
15/05/2014
Rosetta's target comet is becoming active The scientific imaging system OSIRIS on board ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft witnesses the awakening of the mission’s target comet |

|
14/05/2014 - 08:00
Qué es una partícula II: Hawking versus Unruh Esta charla pretende ser una introducción divulgativa a algunos de los fenómenos de la denominada Teoría Cuántica de Campos en espacios curvos. Las dos teorías físicas que, a fecha de hoy, describen las leyes de la naturaleza a un nivel más fundamental son la Relatividad General para el campo gravitatorio, y la Teoría Cuántica de Campos para el resto de campos físicos,... Luis Cortés Barbado Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
24/04/2014 - 14:30
Inconsistences in the harmonic analysis of time series The power of asteroseismology relies on the ability to infer the stellar structure from the unambiguous frequency identification of the correspoinding pulsation mode. Hence, the use of a Fourier transform is in the basis of asteroseismic studies. Nevertheless, the difficulties with the interpretation of the frequencies found in many stars lead us to reconsider Fourier analysis and the classical methods used to process time series... Javier Pascual Granado |

|
23/04/2014 - 10:00
About Mars, its atmosphere and the dust El planeta Marte, con su color rojizo, siempre ha despertado la imaginación de la mente humana en diferentes culturas. Ha sido asociado al dios de la guerra, la destrucción y el inframundo. Ya no tenemos miedo a Marte ni a los marcianos como se tenía antaño, nuestra preocupación ahora es si nuestras naves llegarán al planeta rojo. Este fantástico planeta, el cual estamos descubriendo, tiene la... Dominika Dabrowska Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |