Headlines and events archive
Displaying 1051 - 1100 of 1931
You may also find an archive of news published in the media which are related with the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía - CSIC.
Pages

|
28/11/2012
The planets may exert an influence on the magnetic activity of the Sun The planets could interfere with the mechanisms responsible for generating the solar magnetic field in a key layer of the interior of the star. It would explain other periodicities detected in the solar magnetic activity |

|
22/11/2012
Spanish science and industry meet in the Square Kilometre Array, the largest scientific infraestructure ever developed The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) is a radio telescope made of thousands of antennas distributed over a distance of at least 3000 km. A meeting will analyze the opportunities for Spanish industry in this ambitious project |

|
21/11/2012
A stellar occultation reveals the properties of Makemake The occultation allowed determining the size, shape and albedo of Makemake, and showed that it has no global Pluto-like atmosphere |

|
15/11/2012
Rebirth of X-ray emission from the born-again planetary nebula A30 About 850 years ago, Abell 30 experienced a very late thermal pulse that created a small-scale planetary nebula inside the original one |

|
15/11/2012
Gamma-ray twins strike back MAGIC telescopes re-start observations of the gamma-ray sky after a full upgrade |

|
31/10/2012 - 16:00
Properties and evolution of internetwork magnetic fields inside supergranular cells To understand the formation of small-scale magnetic fields in the quiet Sun and their contribution to the solar activity, it is essential to investigate the properties and evolution of internetwork magnetic fields. Using Hinode/NFI line-of-sight magnetograms of very high sensitivity (6 Mx/cm^{2}), spatial resolution (0.16 arcsec/pixel), and cadence (90 s), we follow the evolution of magnetic elements inside of a supergranular cell located at... Milan Gosic Sala de Reuniones del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |
|
31/10/2012
CALIFA: The local extragalactic universe unveiled The Calar Alto Legacy Integral Field Area survey (CALIFA survey) announces today its first public release of data, offering an unprecedentedly detailed view of one hundred galaxies in the local universe with ample opportunities for scientific study. Together with the data release, two technical publications authored by members of the CALIFA collaboration have been made publicly available, describing the data and showing some of their... |

|
26/10/2012 - 14:00
QSO outflows The study of AGN feedback processes on the evolution of their host galaxies and their environments is a field of growing importance in the past years. One of the feedback mechanisms identified is high-velocity outflows in QSOs. In this talk, some results are presented based on observations of several QSOs, aimed to determine the importance of these outflows as feedback mechanisms. J.Ignacio González Serrano |

|
18/10/2012 - 14:30
Cosmological Challenges of Dwarf Galaxies A prime challenge to our understanding of galaxy formation concerns the scarcity of dwarf galaxies compared with the numerous low-mass halos expected in the current ΛCDM paradigm. This is usually accounted for by assuming that energetic feedback from evolving stars confines dwarf galaxy formation to relatively massive halos spanning a narrow mass range. I will highlight a number of observations that may be used to test this assumption... Julio Navarro |

|
16/10/2012
The first systematic survey of planetary nebula in the solar neighborhood The physical mechanisms responsible for the PN morphological menagerie are still subject of hot debate |
|
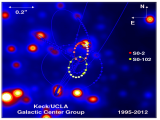
05/10/2012
The shortest known period star orbiting our Galaxy´s supermassive black hole SO-102 revolves around the Milky Way´s supermassive black hole in 11,5 years. The star may help test the laws of gravity under extreme conditions and understand the role supermassive black holes play in the center of galaxies |

|
04/10/2012 - 14:30
Hydrodynamical Models of Core-Collapse Supernovae A set of hydrodynamical models applied to stellar evolutionary progenitors is used to study the nature of core-collapse supernovae (SNe). For the type IIb SN 2011dh, our modeling suggests that a large progenitor star---with R ~200 R_sol--- is needed to reproduce the early light curves. This is consistent with the suggestion that a yellow super-giant star detected at the location of the SN in deep pre-explosion images is the progenitor... Melina Bersten |

|
27/09/2012 - 14:30
ASTRONET, a comprehensive long-term planning for the development of European astronomy ASTRONET was created by a group of European funding agencies, including the Spanish ministry, in order to establish a strategic planning mechanism for all of European astronomy. It covers the whole astronomical domain, from the Sun and Solar System to the limits of the observable Universe, and from radioastronomy to gamma-rays and particles, on the ground as well as in space. ASTRONET aims to engage all astronomical communities... Jesús Gallego |

|
26/09/2012 - 15:00
Ciencia digital transparente: más allá de la automatización La ciencia que se realiza en Astronomía es ciencia digital: cada uno de los elementos y acciones que intervienen en la producción científica podría registrarse en soporte electrónico. Este hecho no impide que el resultado final de un experimento sea aún difícil de reproducir, incluso para el propio autor. La reproducibilidad es uno de los pilares del método científico. En esta charla describiré el trabajo que estamos realizando en el grupo AMIGA... José Enrique Ruiz Sala de Reuniones del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
25/09/2012
Optical surveys miss between 20% and 80% of core-collapse supernova The fraction of core-collapse supernovae that remain undetected due to obscuration by dust reaches one in five for nearby galaxies and four in five for distant galaxies. The number of detected supernovae helps determine the cosmic star formation history |

|
20/09/2012
A galaxy formed 200 million years after the Big Bang MACS1149-JD, a very faint galaxy, will provide clues about the reionization |

|
12/09/2012
Science floods the streets of Granada The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia(IAA-CSIC) coordinates different activities in defense of investment in science: concentrations, a flash mob and outreach on the street to raise awareness of the importance of research. |

|
19/07/2012 - 14:00
A deeper look on thick discs using data from the Spitzer Survey of Stellar Structure in Galaxies (S4G) Thick discs are disc-like components with a scale height larger than that of the classical discs. They are most easily detected in close to edge-on galaxies in which they appear as a roughly exponential excess of light which appears a few thin disc scale heights above the midplane. Their origin has been considered mysterious until recently and several formation theories have been proposed. Unveiling the origin of thick discs is... Sébastien Comerón |

|
16/07/2012
A massive star with the most intense magnetic field yet seen The star's magnetic field, 20.000 times stronger than the Sun's, is slowing the star's rotation |

|
13/07/2012 - 14:00
Jets de Estrellas Jóvenes: Teoría En los últimos años ha habido un gran esfuerzo en la construcción de modelos teóricos que nos permitan entender y explicar distintos aspectos de los jets producidos por estrellas en su vida temprana. Algunos de estos aspectos son: su mecanismo de producción y colimación, la generación de nudos en su interior y la interacción con el medio circundante. En este trabajo se... Jorge Cantó |

|
05/07/2012 - 14:00
Infraestructuras de cálculo en el Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA): pasado, presente y futuro. Actualmente el IAA dispone de una gran infraestructura de cálculo, la conocida Sala Grid, que alberga 32 nodos IBM x3950M2 con un total de 128 procesadores Intel Xeon Quad Core 2.93GHz (512 cores), 4 TeraBytes de memoria RAM, y una capacidad de almacenamiento total de 315 TeraBytes, todo ello interconectado con tecnología de red Infiniband a 20Gbps. Hasta ahora esta infraestructura se ha utilizado dentro del marco del... José Ramón Rodón |

|
28/06/2012
A green look to the sky The Spanish astronomy, technological centers and companies come together in the international project SKA, a network of radioastronomy sensors on a continental scale |

|
21/06/2012 - 14:00
The AGN-Starburst connection in nearby (U)LIRGs: a radio view I review the main results obtained by our team in the last few years, on studies of nearby Luminous and Ultra-Luminous Infrared Galaxies (LIRGs and ULIRGs, respectively). These galaxies are expected to form stars at rates as large as (10-100) Msolar/yr, or even higher, and constitute excellent laboratories for studies of star-formation. They are also expected to be bright at radio wavelengths. Among other results, I will present... Miguel Ángel Pérez Torres |

|
17/06/2012 - 22/06/2012
TEA-IS Summer School Málaga |

|
14/06/2012 - 14:00
Holographic imaging of dense fields: the amazing poor man's MCAO Being able to image large fields at the diffraction limit of large telescopes is one of Astronomy's oldest dreams. The standard way toward achieving this goal is to throw lots of money at it and build ever more sophisticated adaptive optics (AO) systems. As an alternative way, I present an algorithm for speckle holography that has been optimised for diffraction limited imaging of crowded fields. I will present the exciting... Rainer Schoedel |

|
12/06/2012
Gaia-ESO: a revolution in our understanding of the Milky Way and stellar evolution Gaia-ESO, one of the largest and most ambitious ground-based surveys, will study 100.000 stars in our Galaxy |

|
04/06/2012
The most comprehensive global study on the ice The IAA has been involved in the most comprehensive study to date on the ice. The work, which involved 17 scientists from 11 countries collected what are the current issues that exist in this field of research |

|
31/05/2012 - 14:00
NITROGEN-TO-OXYGEN RATIO AS A SOLID TOOL TO ASCERTAIN THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES Nitrogen is one of the most abundant metals in the ISM and thus emitting strong emission-lines in the optical spectrum of ionized gaseous nebulae. Its nucleosynthetic origin is quite different to that of oxygen as it is produced both by massive stars and by intermediate- and low-mass stars. Thus, the study of the nitrogen-to -oxygen ratio by means of especially defined strong-line methods offers a powerful tool to inspect with... Enrique Pérez Montero |

|
31/05/2012
Sierra Nevada Observatory opens its doors Guided tours to the Sierra Nevada Observatory and the Institute of Millimeter Radio Astronomy |

|
26/05/2012 - 15:00
Testeado de Posicionadores de Fibras Ópticas y Desarrollo de Interfaz de Comunicación para Instrumentos de Próxima Generación El Robot comercial de montaje Kawasaki, se baraja como posible brazo posicionador de fibras ópticas para del instrumento OPTIMOS-EVE (E-ELT). La Universidad de Oxford forma parte del consorcio de los espectrógrafos OPTIMOS-EVE y WEAVE (WHT, ambos con elementos retractores de fibras de similar diseño. Como parte de mi proyector fin de máster establecí las bases técnicas para la realización de las... Zaira Modroño Berdiñas Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
24/05/2012 - 14:00
Development of a miniaturized real time attitude controller for micro and nanosatellites In last years low cost space missions have become an instrument for many research institutes to test new technologies and perform low-orbit Earth science using commercial components. Cubesat represent the most popular standard for microsatellites, but due to low cost components and reduced size, there are no complete attitude controllers available for the smallest versions. This talk will describe the development of a control system... Gian Paolo Candini |

|
18/05/2012
PIIISA 2012 - Young people and Science The PIIISA 2012 project ended yesterday. A project that aims to join high school students with the professional investigators. |

|
17/05/2012 - 14:00
Ice Rocks in the Solar System The study of the minor bodies in the Solar System has historically been a major source of information. The term "Minor Body" covers objects exhibiting very different dynamical and compositional characteristics, in fact, every object in the Solar System that is not a planet or a star, is a minor body. All these objects share a common link, they were the building blocks of the Solar System that we observe today and are considered to... Noemi Pinilla Alonso |

|
10/05/2012 - 14:00
The thirteen billion year history of the most massive black holes Super-massive black holes (BHs) that are found in the centers of most galaxies started their growth when the universe was about 300 million years old. Some of these "seed black holes" were probably the remnants of the earliest stars. The largest BHs, that are some 10^10 times more massive than the sun, accumulated most of their mass during the first 3 billion years after the big bang. The less massive ones are still growing today. I... Hagai Netzer |

|
03/05/2012 - 13:00
Detecting substructure in the galactic stellar halo with Gaia We present a Gaia mock catalogue we have created to test various approaches to detect the presence of past mergers in the Galactic halo. We propose an extension of the great circle cell method of Johnston et al. (1996), which is optimized to identify tidal debris along great circles in the sky. We have added the proper motion information that will be supplied by Gaia to add a kinematical restriction to the original method. We test our... Luis A. Aguilar |

|
26/04/2012 - 14:00
The Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3 The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) was installed in 2009 and is now the primary science instrument on HST. Under development since 1998, WFC3 expanded Hubble's ultraviolet and infrared imaging capabilities by factors of more than 20. WFC3 also provides an unparalleled capability for low resolution infrared spectroscopy of very faint sources. This talk will discuss the scientific goals for WFC3, its basic design and technological... John Mackenty |

|
25/04/2012 - 15:00
The Virtual Observatory: The e-Science Environment for Discovery & Collaboration in Astrophysics La astronomía nace cuando el hombre comienza a registrar en diversos medios (tablillas de piedra, papiros, dibujos, fotografías, y recientemente en forma digital) lo que observa en el cielo. En esta charla veremos cómo la cantidad de información accesible a los astrónomos está creciendo de forma exponencial, mientras que su capacidad de procesamiento se está estancando, y que la solución... Juande Santander Vela Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
18/04/2012
Over a hundred researchers meet in Granada to discuss the future of the study of galaxies The workshop, taking place from today until Friday,will delve into a technique that is proving in the study of galaxy evolution,integral field spectroscopy. |

|
12/04/2012 - 14:00
Oxygen in the Universe: a historic introduction We briefly review the main steps that led to the discovery of oxygen in the Universe and to the understanding of its production and cosmic evolution. We highlight some of the problems that still need an explanation. Grażyna Stasińska |

|
11/04/2012
NGC 6778: formation and disruption of a planetary nebula NGC 6778 shows fast collimated outflows which probably resulted in the disruption of the nebular shell and equatorial ring |

|
09/04/2012
The mysterious legacy of Nikola Tesla finally comes to light The Instituto de Astrofisica de Andalucia (IAA-CSIC), one of five institutions selected to spread the material |

|
28/03/2012 - 15:00
Jet wobbling en jets relativistas: el caso del blázar NRAO150 Los jets están presentes en numerosos escenarios astrofísicos. En particular los jets en galaxias con núcleos activos (AGN) son de las fuentes de radiación mas intensas del universo y presentan estructuras observables a longitud de onda de radio que van desde unos pocos parsec a cientos de Kpc. En los últimos años se ha observado en un mayor número de blázares un cambio en la direcci... Sol Natalia Molina Sala de Juntas del Nuevo Edificio (IAA-CSIC) |

|
28/03/2012 - 14:00
A new golden age in Spanish Astronomy: the GTC Spanish Astronomy has experienced a great development during the last 20-30 years, which can be, in part, associated to the available technological resources. Extragalactic astronomy started in Spain due to the agreement for the development of the Observatory of the Roque de los Muchachos, with the installation of the INT 2.5m and WHT 4.2m telescopes and their associated instrumentation. Of course the CAHA... Josefa Masegosa |

|
19/03/2012
The Spanish network of robotic telescopes BOOTES opens its station in China The project, led by astronomers at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia, already has two stations in Spain and one in New Zealand |

|
15/03/2012 - 13:00
What can we learn from gamma-ray anisotropies? Over the last two decades the study of angular anisotropies provided a huge amount of information, when used to analyze the Cosmic Microwave Radiation. The same approach can be extended also to higher energies, studying angular fluctuations in the gamma-ray emission. In this talk I will refer in particular to the data of the Fermi-LAT telescope that has recently presented its measurement of the angular power spectrum (APS) of anisotropies at... Mattia Fornasa |

|
05/03/2012 - 16:00
LINERs, ¿Son también AGNs? Los LINERs (Low Ionization Narrow Emission-line Regions) representan la población más abundante de los AGNs en el Universo local. Se trata de AGNs de baja luminosidad, que podrían resultar ser el nexo de unión entre las galaxias normales y las activas. Haremos un recorrido por las características que muestran los LINERs, tratando de introducirlos en el modelo unificado de AGNs. Lorena Hernández García Sala de Juntas del Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC) |

|
05/03/2012 - 13:00
MIRADAS: The Next-Generation Infrared Spectrograph for the GTC MIRADAS is a near-infrared multi-object R=20,000 echelle spectrograph for the 10.4-meter Gran Telescopio Canarias. It is the most powerful astronomical instrument of its kind ever envisioned, with an observing efficiency more than an order of magnitude greater than current capabilities for 10-meter-class telescopes. The (still-growing) MIRADAS science team includes more than 40 scientists from 8 institutions in the GTC community. In this talk... Stephen Eikenberry |

|
23/02/2012 - 13:00
Seeking and Mocking Non-thermal Emission in Galaxy Clusters Diffuse synchrotron radio emission is observed in many clusters of galaxies probing the presence of high energy cosmic ray (CR) electrons. This emission can be explained by the hadronic model where the electron population originates from the interactions between CR protons and the cluster ambient gas. Additionally, a very high energy gamma-ray emission is also expected. I will briefly review the current knowledge on the non-thermal emission... Fabio Zandanel |

|
20/02/2012
HEXA: the future of sky mapping Today begins a meeting about HEXA, a project for a new 6,5 meter telescope to be located at Calar Alto Observatory (Almería) |

|
16/02/2012 - 13:00
Modelos teóricos de las nebulosas de Eta Carinae En esta plática se presentan modelos teóricos de los eventos eruptivos de 1840 (la gran erupción) y de 1890 (la menor erupción) de la estrella masiva Eta Car. Las nebulosas bipolares en torno a la estrella se formaron de la interacción del material eyectado durante estas erupciones con el viento estándar de la estrella. En nuestros modelos, se supone un escenario de colisión de... Ricardo Francisco González Domínguez |